- PRODUCTS
- COMPANY
- SUPPORT
- PRODUCTS
- BY TYPE
- BY MARKET
- COMPANY
- SUPPORT
Marvell Demonstrates Edge Computing Powered by AWS Greengrass at Arm TechCon 2018
Thanks to the respective merits of its ARMADA® and OCTEON TX® multi-core processor offerings, Marvell is in a prime position to address a broad spectrum of demanding applications situated at the edge of the network. These applications can serve a multitude of markets that include small business, industrial and enterprise, and will require special technologies like efficient packet processing, machine learning and connectivity to the cloud. As part of its collaboration with Amazon Web Services® (AWS), Marvell will be illustrating the capabilities of edge computing applications through an exciting new demo that will be shown to attendees at Arm TechCon - which is being held at the San Jose Convention Center, October 16th-18th.
This demo takes the form of an automated parking lot. An ARMADA processor-based Marvell MACCHIATObin® community board, which integrates the AWS Greengrass® software, is used to serve as an edge compute node. The Marvell edge compute node receives video streams from two cameras that are placed at the entry gate and exit of the parking lot. The ARMADA processor-based compute node runs AWS Greengrass Core; executes two Lambda functions to process the incoming video streams and identify the vehicles entering the garage through their license plates; and subsequently checks whether the vehicles are authorized or unauthorized to enter the parking lot.
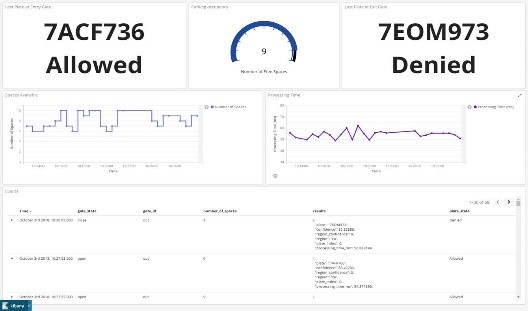
The first Lambda function will be running Automatic License Plate Recognition (OpenALPR) software and it obtains the license plate number and delivers it together with the gate ID (Entry/Exit) to a Lambda function running on the AWS® cloud that will access a DynamoDB® database. The cloud Lambda function will be responsible for reading the DynamoDB whitelist database and determines if the license plate belongs to an authorized car. This information will be sent back to a second Lambda function on the edge of the network, on the MACCHIATObin board, responsible for managing the parking lot capacity and opening or closing the gate. This Lambda function will be logging the activity in the edge to the AWS Cloud Elasticsearch® service, which works as a backend for Kibana®, an open source data visualization engine. Kibana will enable a remote operative to have direct access to information concerning parking lot occupancy, entry gate status and exit gate status. Furthermore, the AWS Cognito service authenticates users for access to Kibana. 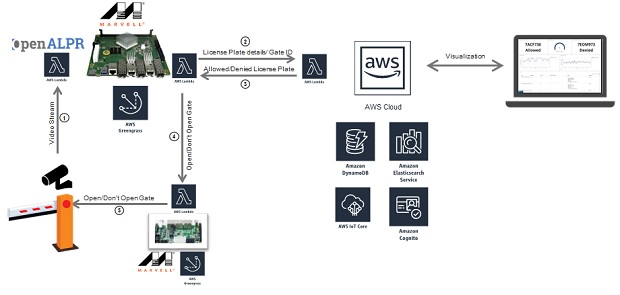
After the AWS Cloud Lambda function sends the verdict (allowed/denied) to the second Lambda function running on the MACCHIATObin board, this MACCHIATObin Lambda function will be responsible for communicating with the gate controller, which is comprised of a Marvell ESPRESSObin® board, and is used to open/close the gateway as required.
The ESPRESSObin board runs as an AWS Greengrass IoT device that will be responsible for opening the gate according to the information received from the MACCHIATObin board’s second Lambda function.
This demo showcases the capabilities to run a machine learning algorithm using AWS Lambda at the edge to make the identification process extremely fast. This is possible through the high performance, low-power Marvell OCTEON TX and ARMADA multi-core processors. Marvell infrastructure processors’ capabilities have the potential to cover a range of higher-end networking and security applications that can benefit from the maturity of the Arm® ecosystem and the ability to run machine learning in a multi-core environment at the edge of the network.
Those visiting the Arm Infrastructure Pavilion (Booth# 216) at Arm TechCon (San Jose Convention Center, October 16th-18th) will be able to see the Marvell Edge Computing demo powered by AWS Greengrass.
Tags: Edge Computing
Recent Posts
- Marvell Named to America’s Best Midsize Employers 2026 Ranking
- Ripple Effects: Why Water Risk Is the Next Major Business Challenge for the Semiconductor Industry
- Boosting AI with CXL Part III: Faster Time-to-First-Token
- Marvell Wins Interconnect Product of the Year for Ara 3nm 1.6T PAM4 DSP
- Improving AI Through CXL Part II: Lower Latency
Archives
Categories
- 5G (10)
- AI (51)
- Cloud (23)
- Coherent DSP (11)
- Company News (108)
- Custom Silicon Solutions (11)
- Data Center (76)
- Data Processing Units (21)
- Enterprise (24)
- ESG (12)
- Ethernet Adapters and Controllers (11)
- Ethernet PHYs (3)
- Ethernet Switching (41)
- Fibre Channel (10)
- Marvell Government Solutions (2)
- Networking (45)
- Optical Modules (20)
- Security (6)
- Server Connectivity (36)
- SSD Controllers (6)
- Storage (23)
- Storage Accelerators (4)
- What Makes Marvell (47)
Copyright © 2026 Marvell, All rights reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Contact

