

By Kim Markle, Director Influencer Relations, Marvell
Wind River and Marvell have collaborated to create an open, virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN) solution for communication service providers (CSPs) that offers cloud scalability with the features, performance, and energy efficiency of established 5G networks. The collaboration integrates two complementary, industry-leading technologies—the Marvell® OCTEON® 10 Fusion 5G baseband processor and the Wind River Studio cloud software—to provide the carrier ecosystem a deployment-ready vRAN platform built on technologies that are widely proven in 5G networks and data centers.
CSPs aim to leverage established IT infrastructure for enhanced service agility and streamlined DevOps in the cloud-native RAN. Marvell's OCTEON 10 Fusion processor supports these goals with programmability based on open-source, industry-standard interfaces and integration with leading cloud software platforms such as Wind River Studio.
To ensure open-source distribution of Wind River Studio software, OCTEON 10 Fusion software drivers are being used by StarlingX, an open development and integration project. Marvell’s drivers enable Wind River Studio software to communicate with and control the OCTEON 10 Fusion processor. This facilitates developer access to an optimized vRAN system that offers new options for CSPs and helps to expand the carrier ecosystem of RAN and data center hardware and software suppliers, as well as system integrators.
By Peter Carson, Senior Director Solutions Marketing, Marvell
5G networks are evolving to a cloud-native architecture with Open RAN at the center. This explainer series is aimed at de-mystifying the challenges and complexity in scaling these emerging open and virtualized radio access networks. Let’s start with the compute architecture.
Open RAN systems based on legacy compute architectures utilize an excessively high number of CPU cores and energy to support 5G Layer 1 (L1) and other data-centric processing, like security, networking and storage virtualization. As illustrated in the diagram below, this leaves very few host compute resources available for the tasks the server was originally designed to support. These systems typically offload a small subset of 5G L1 functions, such as forward error correction (FEC), from the host to an external FPGA-based accelerator but execute the processing offline. This kind of look-aside (offline) processing of time-critical L1 functions outside the data path adds latency that degrades system performance.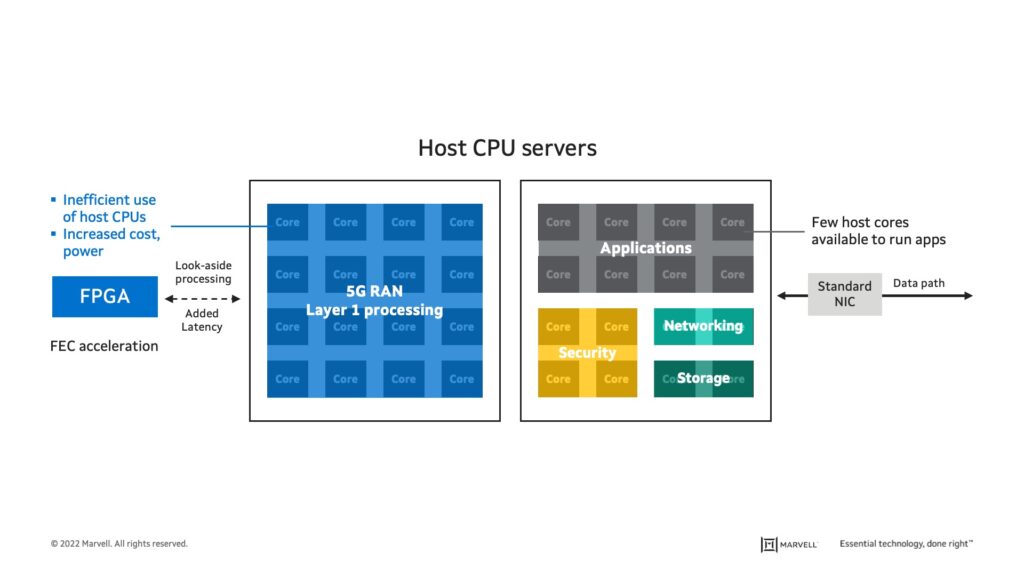
Image: Limitations of Open RAN systems based on general purpose processors
Copyright © 2025 Marvell, All Rights Reserved
